
PYROCLASTICS, BIG BEND.
VOLCANIC STRUCTURES
Two aspects of volcanism
are relevant to the study of geomorphology:
1. There are a number of volcanic features that in themselves constitute unique
landforms - various types of volcanoes and craters being the most obvious
examples.
2. Igneous rocks, whether intrusive or extrusive, in layers or in masses, form
distinctive components of local geology, which can contribute to landscape
development via differential erosion.
Volcanic Cones and Craters. The style of a volcanic eruption and the nature of the volcanic features it produces depends primarily on the characteristics of the magma. 1. GRANITIC magma (usually formed in subduction zones) is very viscous and does not flow easily; near the surface it solidifies quickly, often causing blockages of the vent and explosive eruptions,

PYROCLASTICS, BIG BEND.
resulting in pyroclastic deposits. These deposits consist of volcanic fragments ranging in size from fine ash to large boulders. Successive eruptions result in an accumulation of volcanic rock surrounding the vent, producing a VOLCANIC CONE.
CINDER CONES: are
produced by the eruption of viscous magma and are composed almost entirely of
pyroclastic deposits. These angular fragments form steep (30-40o) and
usually small
(< 1000') cones.

CINDER CONE, ARIZONA.
COMPOSITE CONES (or STRATOVOLCANOES): consist of alternating layers of viscous lava flows and pyroclastic deposits in a relatively steep-sided cone, commonly reaching over 10 000' in height.
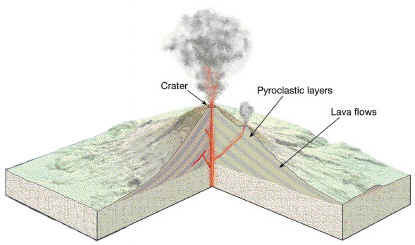
COMPOSITE CONE
Most volcanic cones have craters at the top, due to erosion or collapse of rocks surrounding the vent during eruptions; however, CALDERAS are much larger volcanic craters caused by particularly large and explosive eruptions.
The caldera is formed by removal of material in the eruption and by collapse of the surface into the magma chamber. Crater Lake, Oregon, is the site of the former volcano Mt. Mazama which erupted explosively about 6800 years ago.
2. Fluid BASALTIC magma (usually formed over hot spots) flows very readily and therefore does not usually erupt explosively and form pyroclastic deposits.Instead the lava tends to spread out forming large gently sloping cones or extensive layers. The cones are SHIELD VOLCANOES, which form on the ocean floor above hot spots. The most famous example is Hawaii, consisting of 5 shield volcanoes joined together. The largest of these, Mauna Loa, rises 30,077' from the ocean floor.
Igneous Rocks As
Geological Components
Igneous rocks contribute to local geology in 3 ways:
1. Plutons,
2. Flood Basalts
3. Pyroclastic Flow Deposits
Plutons. Most igneous rocks are INTRUSIVE, in other words they are created below the surface forming masses of rock collectively known as PLUTONS.
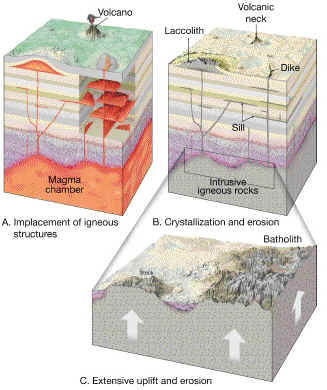
PLUTONS.
These contribute to geomorphology when they are exposed at the surface after the overlying rocks are worn away. Most igneous rock, such as granite, is usually of relatively high resistance - therefore many exposed plutons form high relief features due to differential erosion.
LACCOLITHS are smaller dome-shaped masses intruded between pre-existing rock layers. Often the country rock is deformed into a dome by the intrusion.Exposed laccoliths may also form resistant uplands.
A DYKE is a near-vertical layer intruded along a fracture in pre-existing rock. Often dykes radiate from volcanic necks, such as Ship Rock, N.M., which is a volcanic neck (plugged vent of a former volcano), from which the softer cone has eroded away.
A SILL is the horizontal equivalent of a dyke, intruded horizontally between layers of pre-existing rock.

SILL
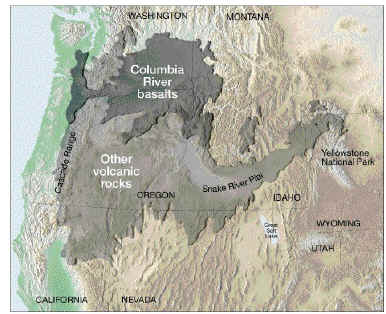
Flood Basalts
Lava flows on the surface tend, for the most part, to be basalt, because it is
fluid and capable of flowing over large areas, especially if erupted from a long
fissure rather than a single vent.Repeated eruptions of basaltic lava forms
FLOOD BASALTS, which can build up to great thicknesses and cover very large
areas, such as the Columbia Plateau of the Pacific Northwest. Flood basalts can
erode like horizontal strata, forming canyons with "stepped" sides.
Pyroclastic Flow Deposits
Pyroclastic (ash, dust, rocks) flows can form thick deposits over large areas. A wide range of rocks are included from compacted, welded ash (tuff), which can be quite erodable, to resistant volcanic debris flow conglomerates.

RYHOLITIC LAVA OVER ASH FLOW OVER VOLCANIC
DEBRIS FLOW CONGLOMERATE, BIG BEND.
If pyroclastics are mixed with water (eg. melting ice/snow), LAHARS can form (volcanic debris flows). Lahars caused much of the destruction in the eruption of Mt. St. Helens (May 18th, 1980). All types of pyroclastic flow can fill in pre-existing valleys or form layers, which then become part of the geology and contribute to differential erosion.